May 20, 2025 Blockchain
Blockchain for Enterprises: Real-World Use Cases and Implementation Strategy
May 20, 2025 Blockchain
Table of Contents
May 20, 2025 Blockchain
Blockchain for enterprises is one such gift that brings more trust and cooperation among stakeholders, both out and within the organizational walls.
It’s not merely about cryptocurrencies. It is a matter of creating secure, transparent and efficient mechanisms.
“Blockchain is the tech. Bitcoin is merely the first mainstream manifestation of its potential.” — Marc Kenigsberg
That is what this quote is trying to say about the increased use of blockchain beyond cryptocurrency. It is starting to be realized by businesses in all fields. Imagine a supply chain in which every move has got a record and is non-reversible. Picture data sharing without intermediaries. Enterprise blockchain is the promise of this.
Did you know?
According to an analysis of Enterprise Blockchain Market, the size of the market was 9.64 billion in 2023, and it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 47.4% till 2030 to reach 145.9 billion in 2030.
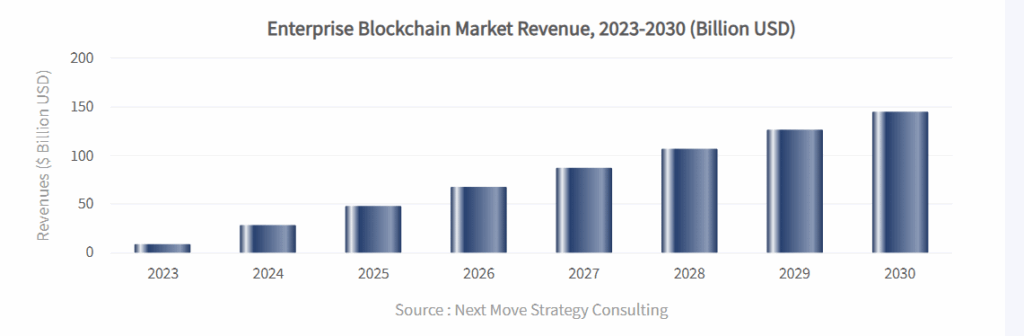
This isn’t hype. Companies are adopting blockchain solutions. They are simplifying processes, increasing safety, and creating more trust between partners and customers.
We understand how getting a new technology can appear to be intimidating. That explains why we are going to simplify it. This blog shall dive into the curious world of Blockchain for Enterprises. We will demystify what it is and why it is important. Here we are going to look at real-world applications, working advantages, and beyond.
Let us start and establish some fundamentals. Starting with:
Blockchain for Enterprises represents the application of blockchain in intra-organizational setups outside the public and permissionless environments it is mostly used in association with cryptocurrencies.
Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, enterprise blockchains are typically permissioned or private, where access to the network is granted and limited to authorised parties.
Main features of Blockchain for Enterprises are:
Such decentralization is a built-in property of blockchain for enterprises with greater security and trust.
Every block in the chain contains a bunch of verified transactions, and once a block has been added to the chain, it is impossible to change or remove it, thus securing the stored data.
Let’s acquire this through an example:
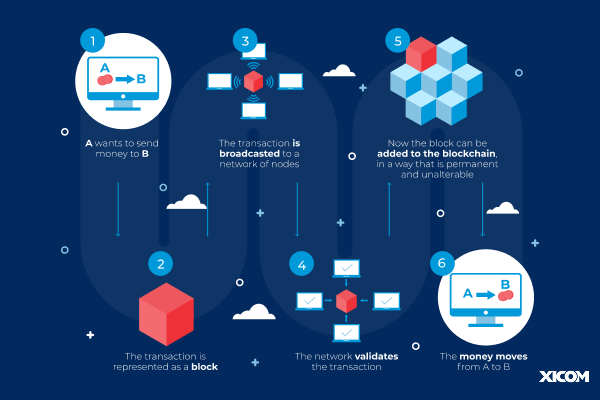
Suppose A wants to pay B. This is how a blockchain facilitates it:
Now, let’s discuss the different types of enterprise blockchain networks.
Besides, there are four main types of enterprise blockchain networks to facilitate different organizational needs and various access management levels. They are:
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain (Permissioned) | Consortium Blockchain (Permissioned) | Hybrid Blockchain |
| Control | No single entity controls the network. | Single organization controls the network. | Group or consortium of organizations governs. | Combination of centralized and decentralized control. |
| Access | Permissionless: Anyone can join and participate. | Permissioned: Only authorized participants. | Permissioned: Only authorized participants. | Permissioned private part with potential public interaction. |
| Transparency | High: All transactions are typically public. | Controlled: Visibility can be restricted. | Controlled: Visibility is shared among consortium members. | Variable: Transparency depends on the specific design. |
| Decentralization | High: Distributed across a large number of nodes. | Lower: Centralized control within the organization. | Medium: Decentralized among consortium members. | Variable: Decentralization depends on the specific design. |
| Scalability | Often lower due to the need for broad consensus. | Potentially higher as the network is controlled. | Potentially higher than public blockchains. | Variable: Scalability depends on the specific design. |
| Trust Model | Trust is achieved through transparency and code. | Trust is placed in the controlling organization. | Trust is distributed among consortium members. | Variable: Trust model depends on the specific design. |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies, some decentralized applications (dApps). | Internal enterprise applications, supply chain management (within a single organization), asset tracking. | Industry-wide collaborations, supply chain management (across multiple organizations), trade finance. | Applications requiring both privacy and public interaction, specific data sharing with broader networks. |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin. | Hyperledger Fabric, R3 Corda (some implementations). | R3 Corda (some implementations), Quorum. | Often custom-built solutions tailored to specific needs. |
Now, we will cover what specific components of enterprise blockchain make this transformative potential a reality for businesses.
Learning about the basic building blocks will be fundamental in terms of understanding the potential of blockchain for enterprises.
The flexibility of the blockchain for enterprises has seen it play a role in so many sectors, with customized solutions to particular industry issues. Many top blockchain use cases for enterprise, we shall see here:
The revolution of supply chain management is among the most promising enterprise use cases for blockchain. With the use of blockchain, a transparent yet immutable proof of the journey of a product is possible, and thus, the tracking of goods and materials from origin to end consumer (consumer) is made possible. This enhances traceability and accountability.
For instance, in the food business, blockchain is capable of tracking the origin and management of the products, ensuring they are safe and earning the trust of the consumer. One of the real-world applications is the use of blockchain, IoT, and cognitive analytics at Golden State Foods. CTO Guilda Javaheri and her team are providing quick-serve restaurants with an unmatched view into how food gets to the customer every step of the way.
Similarly, the pharmaceutical enterprises can use the blockchain, augmented by AI in the supply chain, as an extended traceability and anti-counterfeit measure to give auditable and secure records against counterfeit drugs.
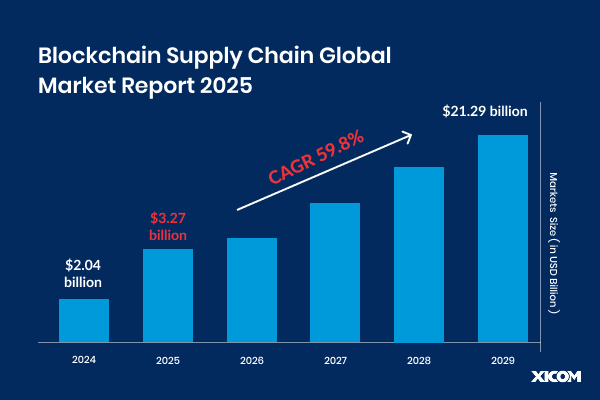
Apart from everything, the market size of the blockchain supply chain has been exponentially expanding in recent years. It will increase from $2.04 billion in 2024 to $3.27 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 60.1%.
To help such transformation, numerous enterprises seek help from a reliable software development company for full-cycle implementation.
Blockchain technology has lots of enterprise use cases that are being explored by the financial services industry. In this case, the adoption of digital currency is the area where the largest amount of blockchain is used, followed by smart contracts, cross-border payments, and the storage of customer data.
Along with that, some other major use cases of blockchain in finance are:
Another important use is the enhancement of Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) processes, where blockchain creates a safe and auditable way of managing digital identities.
Moreover, the blockchain for enterprises is implemented to automate the trade finance processes and letters of credit, minimize paperwork and the time for the transactions.
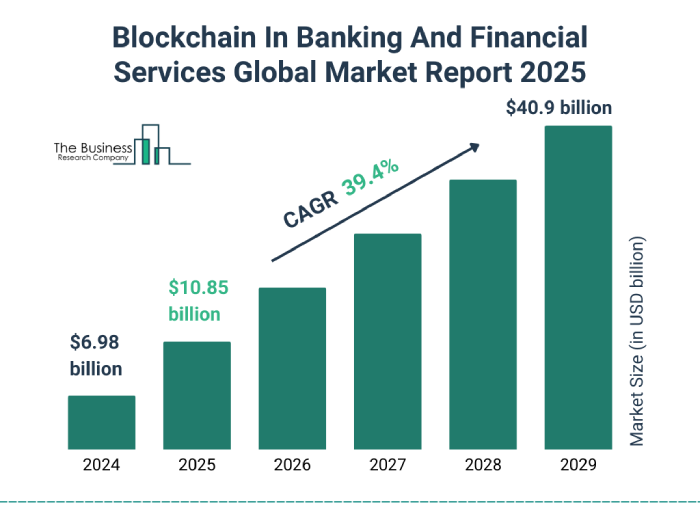
Nevertheless, the blockchain in the banking and financial services market size has grown exponentially in recent years. It will increase from USD 6.98 billion in 2024 to USD 10.85 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 55.3%.
Digital identity management built on blockchain provides better security and control for individuals as well as institutions. To explore this further, check out our blog on Blockchain in Banking.
Additionally, our blog on Blockchain in Trade Finance highlights how such applications are transforming cross-border transactions and boosting transparency in the financial ecosystem.
The research report has identified that the market for blockchain in healthcare will be boosted by increased investments, the need for securing data, and the need for efficient operations in healthcare.
According to a recent report, the global market size of blockchain technology in healthcare is estimated to be USD 7.04 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 63.3% for 2024–2030 period.
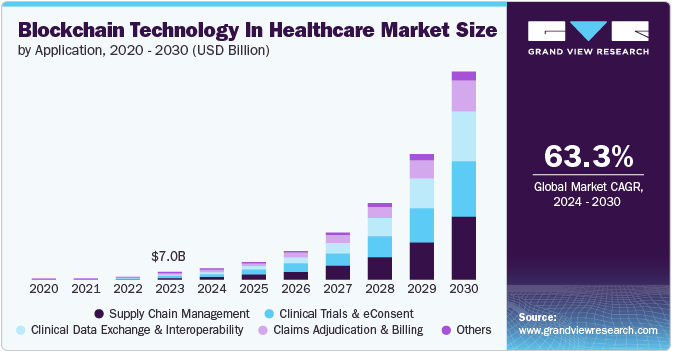
Blockchain for enterprises provides transformational opportunities in healthcare. Safety of handling and accessing patient health records is of the essence and blockchain provides a decentralized and encrypted system of handling these records.
Managing clinical trial data, making sure that it is consistent and cannot be modified, is another essential enterprise use case for blockchain.
Also, among other main use cases of blockchain in healthcare, we can mention the following ones:
These applications of blockchain technology create enhanced data privacy, increased interoperability between healthcare systems and decreased circulation of fake drugs in the market. Our points about the healthcare business ideas may provide a wider vision.
Blockchain can provide more security and verifiability to educational credentials and records. Some of the use cases of blockchain in the education sector are:
There are several ways through which the automotive industry can benefit from Blockchain. Blockchain is changing how cars are being built, sold, maintained and operated due to its capability to provide transparency, security and real-time traceability.
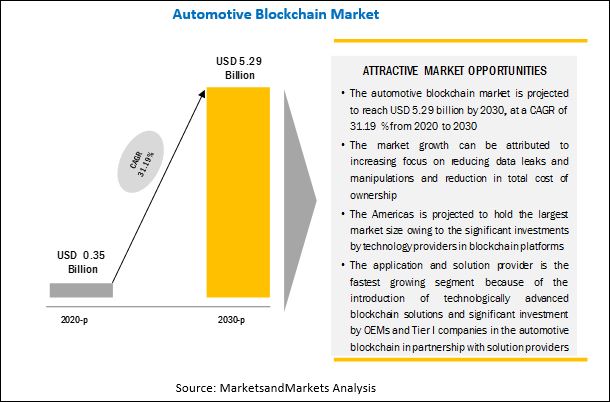
The global blockchain in automotive market will grow by 5.29 billion USD, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 31.19% from 0.35 billion USD in 2020 during the period between 2020 to 2030, according to a report by MarketsandMarkets
You know, such things as BaaS, cryptocurrency, and ICOs are very ready to rock the market of automotive blockchain. They’re not just buzzwords; they are going to actually make business processes much smoother.
Imagine having such a system that increases the level of transparency and keeps everything secure, due to distributed ledger technology. It’s quite cool if you think of it. What is more, what seller would not like faster transactions and less total cost of ownership? It is a win-win situation for all the parties involved.
Among the main use cases are the following:
According to PwC, the aviation industry can also reduce spending on maintenance by up to $3.5 billion a year with the use of blockchain technology. For the aviation businesses that want the most innovative solutions, collaboration with a reputable mobile app development company in India is a wise choice.
These companies have special technological capabilities that can carry out custom blockchain solutions that reflect the specific requirements of the aviation industry.
Conventional systems have challenges with part authenticity, disintegrated data, and handwritten maintenance logs-in. Blockchain overcomes these problems with a secure ledger that is shared.
Some common enterprise use cases of blockchain in aviation:
Blockchain technology for enterprises is rapidly catching on the retail outlets to change operations, increase confidence of consumers, and streamline logistics. Some of the leading blockchain use cases for enterprise include the transparency of the supply chain, a key game-changer.
Food items tracking of purchase from the farm to the shelf is possible in real time by retail giants like Walmart and Carrefour through blockchain. This limits spoilage, recalls, and fraud, and opens full visibility into the sourcing of the product to the consumer.
Management of loyalty programs is also an emergent use case. Instead of having a variety of loyalty systems to deal with, retailers are now developing blockchain-based platforms that allow easy point building and release among the stakeholders.
Online payment frauds, too, are being tackled using the real-time verification abilities of the blockchain.
More than 56% of the retail executives (Deloitte) think blockchain is a fundamental strategic initiative in innovation and customer experience.
The real estate business has been plagued by murky deals, tardy clearance, and title irregularities for a long time. Nowadays, blockchain is introducing a new age of trust in a digital world.
Through the digitization of records of ownership of property, automation of contracts, and facilitating cross-border deals, blockchain makes it easier for buyers, sellers, and agents to eliminate friction and increase the speed of transactions. It also allows advanced investment structures such as tokenization, where real estate becomes easily accessible yet transparent as never before.
Some of the common enterprise use cases for blockchain in real estate:
Deloitte states that US$4 trillion of property will be tokenized by 2035, growing from less than US$0.3 trillion in 2024, at a CAGR of 27%.
Forward-thinking firms now hire software developers with blockchain expertise to future-proof their property tech solutions.
As the media industry is facing an increased challenge from streaming, digital piracy, and content monetization, transformation is inevitable at the backdrop of blockchain technology for enterprises.
From establishing ownership rights to automating the payout of royalties, blockchain allows the creators to have control over their intellectual property while boosting transparency and fairness. By using the middlemen and guaranteeing the real-time compensation, blockchain is transforming the way artists, musicians, and filmmakers stay connected to fans and benefit from their works.
Top blockchain use cases for enterprise in media:
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce estimates $29 billion in annual losses in terms of piracy, making blockchain adoption a necessity in financial terms.
A great many entertainment startups and production houses would now seek help from a first-class blockchain development company as their partner in developing creator-first, secure platforms.
Such full details of the examples demonstrate the wide scope and the effectiveness of Blockchain in Enterprises of all industries. As the technology matures, as well as its adoption, we can see even more innovative enterprise use cases of blockchain.
Now, let’s find out why blockchain is important for enterprises. In short, it has incredible benefits.
Here’s a brief how-to for deploying blockchain to your company:
With an effective strategy, Blockchain for Enterprises is converted into a game-changer. With the selection of the appropriate enterprise use cases for blockchain, the development of secure and scalable networks, and their readiness to follow new trends, companies can transform their activities.
Blockchain is revolutionizing the enterprise scene, be it transparency of the supply chain, seminal digital identities, or fraud-proof records. With this adoption increasing, it is wise to invest wisely and place your organization at the forefront of digital innovation.
Depending on complexity, features, selected platform, location of the developer, and integration needs, the cost is quite different. However, the cost of developing a simple blockchain app can roughly range from $40,000 to $80,000.
Privacy for guarding sensitive information, good defense against hackers, enough throughput to support efficient performance, and optimum cost of operations.
– Ethereum (general-purpose smart contracts)
– Hyperledger Fabric (permissioned and modular)
– Quorum (privacy-enabled version of Ethereum)
– Corda (for regulated industries)
– XDC Network (hybrid for cross-border trade)
– Hyperledger Sawtooth (flexible and scalable)
It will depend on an end-to-end analysis of the business’s specific requirements, ranging from privacy, scalability requirements, level of decentralization desired, compliance requirements, and the very use case to be solved. Proof-of-concept (PoC) might be helpful to prototype across platforms.
The legal and regulatory environment in which blockchain technology is evolving. Enterprises must take into account data privacy legislation (such as GDPR), sector-specific legislation (such as finance or healthcare), and the enforceability of smart contracts from a legal perspective in their jurisdiction.